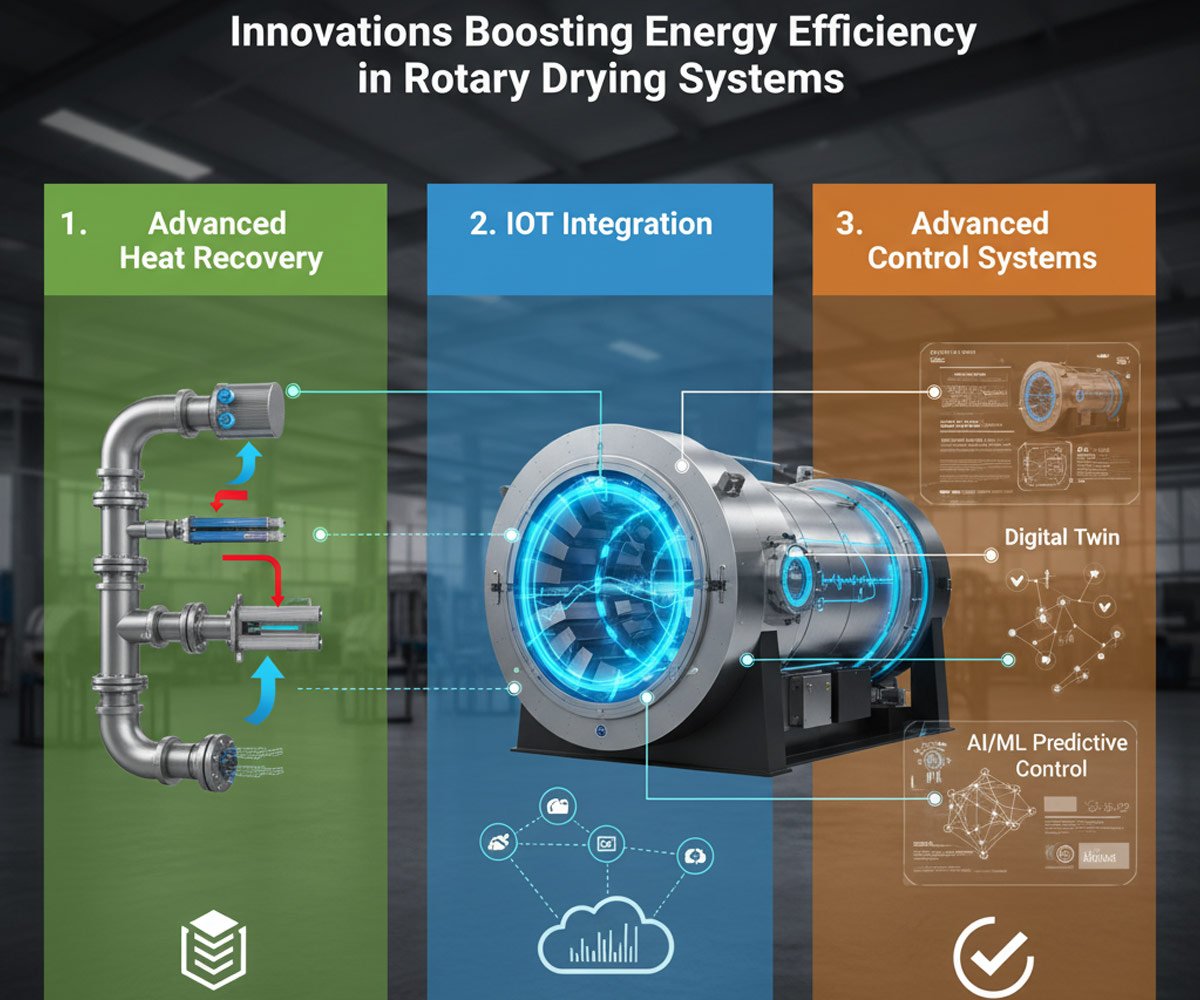
1. Advanced Heat Recovery Systems
This is perhaps the most impactful area for energy savings. Waste heat from the dryer’s exhaust is a significant source of energy loss in traditional systems.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR):
- Innovation: A portion of the hot, moisture-laden exhaust gas is mixed with fresh ambient air and recirculated back into the drying chamber. This reduces the amount of fresh air that needs to be heated from scratch.
- Benefit: Reduces fuel consumption, lowers emissions, and can improve drying kinetics by maintaining a higher humidity in the drying air (for certain products).
- Air-to-Air / Air-to-Water Heat Exchangers:
- Innovation: Dedicated heat exchangers transfer thermal energy from the hot exhaust gas to the incoming fresh air (pre-heating it) or to water/thermal oil for use elsewhere in the plant (e.g., pre-heating feedstock, space heating).
- Benefit: Captures and reuses significant amounts of waste heat, drastically cutting fuel requirements.
2. IoT Integration and Real-time Monitoring
The Internet of Things (IoT) provides the data backbone for smart, efficient operations.
- Extensive Sensor Networks:
- Innovation: Deployment of numerous sensors measuring parameters like inlet/outlet temperatures, moisture content (inlet/outlet), airflow rates, drum speed, fuel consumption, and even vibration analysis.
- Benefit: Provides a comprehensive, real-time overview of the dryer’s performance, enabling operators to identify inefficiencies or potential issues instantly.
- Cloud-Based Data Analytics:
- Innovation: Data collected from IoT sensors is uploaded to cloud platforms for storage, analysis, and visualization. Advanced algorithms can identify trends, anomalies, and opportunities for optimization.
- Benefit: Facilitates data-driven decision-making, predictive maintenance, and remote monitoring/troubleshooting.
3. Advanced Control Systems (AI/ML & Digital Twins)
Beyond basic PID control, modern systems leverage computational power to optimize performance dynamically.
- Predictive Control (AI/ML):
- Innovation: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms learn from historical and real-time data to predict optimal operating parameters. They can anticipate changes (e.g., in feedstock moisture, ambient temperature) and adjust the dryer’s settings proactively.
- Benefit: Maintains optimal drying conditions, prevents over-drying (which wastes energy), ensures consistent product quality, and minimizes energy consumption.
- Digital Twins:
- Innovation: A virtual, real-time replica of the physical rotary dryer. It uses sensor data to simulate current performance and predict the impact of parameter changes.
- Benefit: Allows for virtual experimentation to find the most energy-efficient operating points without risking actual production. Enables predictive maintenance and optimized scheduling.
4. Optimized Drum Design and Material Handling
Improvements in the physical design of the dryer itself also contribute to efficiency.
- Improved Flight Designs:
- Innovation: Redesigned internal flights (lifters) that more effectively cascade the material through the hot air stream, maximizing heat transfer and minimizing “slip” (material sliding along the drum bottom).
- Benefit: Ensures more uniform drying, reduces drying time, and prevents inefficient tumbling.
- Insulation and Sealing:
- Innovation: Enhanced insulation materials for the drum and improved sealing mechanisms at the inlet and outlet.
- Benefit: Minimizes heat loss to the ambient environment and prevents unwanted air ingress/egress, maintaining stable drying conditions and reducing energy waste.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs):
- Innovation: Using VFDs to control the speed of the main drive motor, fans, and blowers.
- Benefit: Allows operators to precisely match motor speed to process requirements, leading to significant energy savings compared to constant-speed motors, especially during partial load operations.
By integrating these innovations, modern rotary drying systems are becoming increasingly intelligent, self-optimizing, and environmentally friendly, delivering higher throughputs with significantly lower energy costs.