Rotary dryers are highly versatile, continuous-operation industrial machines used to reduce the moisture content of bulk solids by bringing them into contact with a heated gas. Due to their robust design and capacity to handle large volumes of material, they are essential across numerous heavy and process industries.
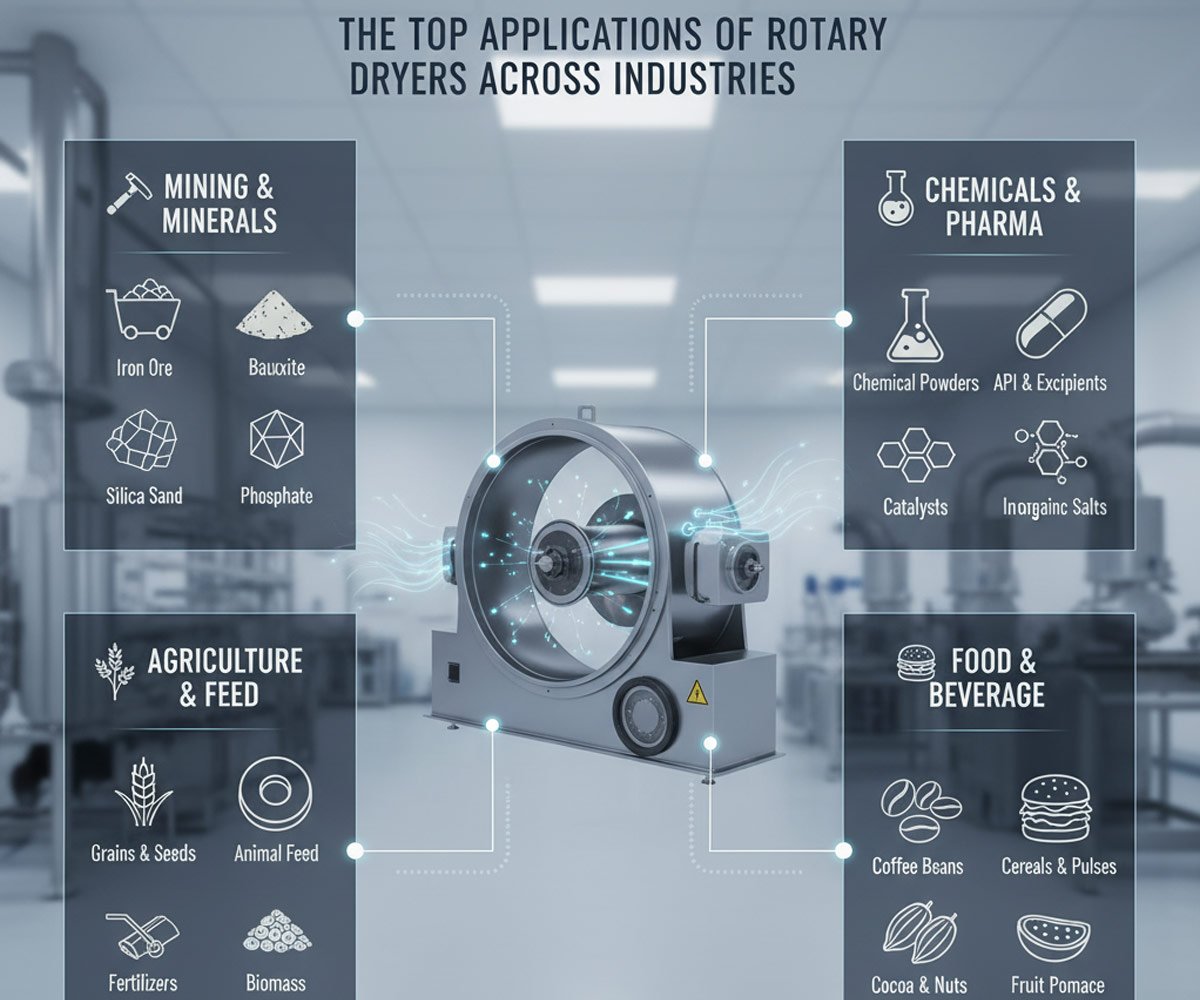
Here are the top applications of rotary dryers across key sectors:
Mining, Minerals, and Aggregates
The mineral industry is one of the most common users of rotary dryers, leveraging their heavy-duty construction to handle abrasive and high-volume materials.
- Ore and Mineral Processing: Drying minerals like bauxite, copper ore, iron ore, potash, phosphate rock, and silica sand is crucial before further grinding, processing, or transportation. Drying minimizes weight for shipping and prepares the feedstock for chemical extraction processes.
- Aggregates: Drying materials like sand, stone, and clays for use in construction, ceramics, and other industrial applications.
- Specialty Materials: Processing materials like gypsum and limestone that are also frequently used in fertilizer and soil amendment applications.
Agriculture and Animal Feed
In the agricultural sector, rotary dryers ensure the quality, preservation, and stability of bulk products, often dealing with high-moisture content materials.
- Grain and Seed Drying: Drying post-harvest crops like corn, wheat, soybeans, and other grains prevents fungal growth, spoilage, and germination, ensuring long-term storage and preservation of nutritional value.
- Fertilizer Production: Rotary dryers are critical for drying various fertilizers, including organic fertilizers (like processed manure), and inorganic compounds like NPK, DAP (Di-ammonium Phosphate), and Ammonium Sulfate. Drying prevents caking, improves particle hardness, and extends shelf life.
- Animal Feed: Removing moisture from feed ingredients and byproducts like citrus pulp, DDGS (Distiller’s Dried Grains with Solubles), and various oilseeds preserves nutrients, controls microbial growth, and reduces transportation costs by allowing for pelletizing.
- Biomass: Drying wood chips, sawdust, straw, and other biomass materials for use in energy production or pellet manufacturing.
Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals
Rotary dryers offer the necessary control and capacity for large-scale chemical processes, often employing indirect heating to prevent contamination or degradation of sensitive compounds.
- Chemical Processing: Drying bulk powdered chemicals such as gypsum and various inorganic chemicals. They are also used for tasks beyond simple drying, serving as granulators or coolers.
- Catalysts and Adsorbents: Processing materials where a specific particle size distribution or texture is required. Indirect drying is often preferred here.
- Pharmaceuticals (Excipients and API): In the production of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and excipients (inactive ingredients), controlled rotary drying ensures uniform moisture removal, maintains ingredient integrity, and meets strict quality assurance standards.
Food and Beverage
For food products, rotary dryers are used for granular materials where uniform heating is important to prevent burning or loss of quality.
- Grains and Cereals: Drying cereals, pulses, and coffee beans.
- Food Byproducts: Drying food processing wastes or byproducts for re-use.
- Roasting: Sometimes modified for roasting processes involving cocoa beans or nuts.
Rotary dryers are often chosen over other drying technologies because of their high capacity, durability, continuous operation, and tolerance to variations in feedstock size and moisture content.