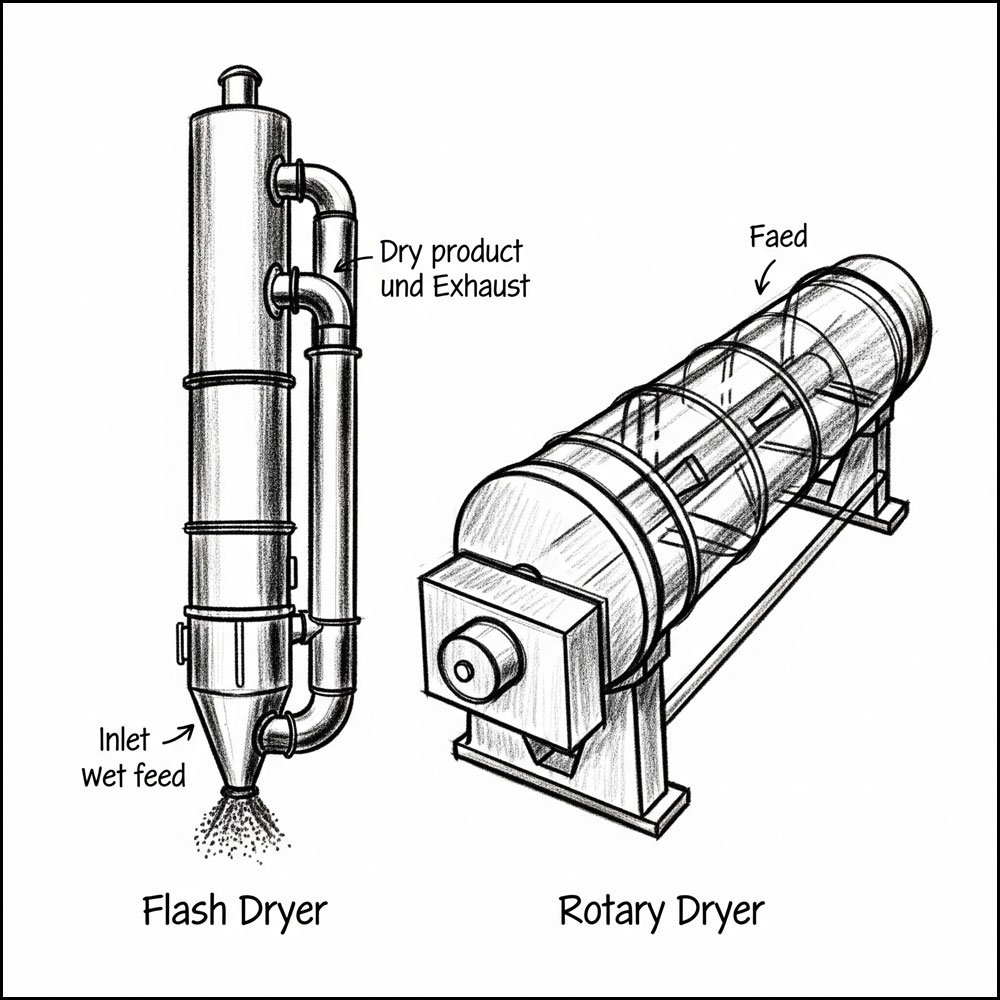
Aksh Engineering, a leading provider of industrial drying and evaporation systems, offers a range of high-performance dryers, including both flash dryers and rotary dryers. While both technologies are designed to remove moisture from materials, they operate on distinct principles and are suited for different applications. This comparison highlights the key features, advantages, and ideal uses for each type of dryer, as manufactured by Aksh Engineering.
Flash Dryers
Flash dryers, also known as pneumatic dryers, are designed for the rapid and efficient drying of fine, heat-sensitive materials. Aksh Engineering’s flash dryers, including their specialized Swirl Agitated (Spin) Flash Dryers and Cage Mill Flash Dryers, excel in processing challenging materials.
Working Principle
The core principle of a flash dryer is to instantly evaporate moisture by dispersing wet material into a stream of hot gas. The extremely short residence time (often just a few seconds) and the large surface area created by the dispersed particles ensure rapid drying while minimizing the risk of thermal degradation.
- Swirl Agitated (Spin) Flash Dryer: This type is specifically designed for sticky, pasty, and thixotropic filter cakes. A mechanical agitator at the base of the drying chamber creates a swirling, fluidized bed of material. This intense agitation breaks down agglomerates and ensures excellent contact between the wet material and the hot air, allowing for quick and uniform drying.
- Cage Mill Flash Dryer: This system is ideal for materials that are lumpy, hard, or have a tendency to crust during drying. The cage mill simultaneously de-agglomerates and dries the material in a continuous, high-speed process. The mechanical action breaks down wet lumps, exposing new surfaces for efficient drying and often eliminating the need for a separate upstream milling process.
Key Features and Advantages
- High Drying Efficiency and Speed: Flash dryers are known for their fast drying process, which significantly reduces processing time.
- Gentle Drying: The very short residence time and evaporative cooling effect prevent the product itself from reaching high temperatures, making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials like pharmaceuticals, food products, and specialty chemicals.
- De-agglomeration: Aksh Engineering’s specialized flash dryers (Spin and Cage Mill) are highly effective at handling cohesive and lumpy feeds, producing a fine, free-flowing powder.
- Customizable Designs: Aksh Engineering offers various customizable options, including adjustable airflow, temperature control, and different feed conditioning equipment to handle materials with a wide range of moisture content (from 5% to over 87%).
- High Product Quality: The uniform drying process results in a consistent particle size distribution, which is crucial for many applications.
Rotary Dryers
Rotary dryers, also known as rotary drum or tumbling dryers, are a robust and reliable solution for large-capacity drying applications. Aksh Engineering’s rotary dryers are designed for continuous, heavy-duty industrial operations.
Working Principle
A rotary dryer consists of a large, rotating cylindrical shell that is slightly inclined. Wet material is fed into the higher end, and as the drum rotates, internal flights or lifters tumble the material, showering it through a stream of hot gas. This continuous tumbling action ensures efficient heat and mass transfer, leading to moisture evaporation.
- Airflow Configuration: Aksh Engineering offers both co-current (hot air and material flow in the same direction) and counter-current (hot air and material flow in opposite directions) designs. Co-current is often recommended for heat-sensitive materials, while counter-current provides higher thermal efficiency for robust materials.
Key Features and Advantages
- High Throughput and Capacity: Rotary dryers are well-suited for large-scale operations, with Aksh Engineering designing systems to handle capacities from a few hundred kilograms to several tons per hour.
- Robust and Durable Construction: Engineered for heavy-duty use, Aksh’s rotary dryers are built to withstand challenging conditions and handle abrasive or high-temperature materials with low maintenance requirements.
- Variable Moisture Content: This technology can efficiently handle materials with high initial moisture content and dry them to low final moisture levels.
- Effective for Uneven Particle Size: Rotary dryers are ideal for feeds with a wide or uneven particle size distribution.
- Energy Efficiency Optimization: Aksh Engineering’s designs focus on maximizing thermal efficiency through intelligent flight designs and precise control systems.
Flash Dryer vs. Rotary Dryer: A Direct Comparison
| Feature | Flash Dryer (Aksh Engineering) | Rotary Dryer (Aksh Engineering) |
| Material Type | Fine powders, sticky pastes, filter cakes, and heat-sensitive materials. | Bulk materials, granules, and materials with uneven particle size distribution. |
| Drying Time | Very short (seconds). | Longer (minutes to hours). |
| Operating Principle | Instantaneous drying by dispersing material in a hot gas stream. | Tumbling material in a rotating, inclined cylindrical shell. |
| Moisture Content | Can handle high moisture content, especially with special agitators. | Efficiently handles a wide range of moisture contents. |
| Capacity | Suitable for a wide range of capacities, with specialized designs for difficult feeds. | Primarily used for large-scale, high-capacity applications. |
| Final Product | Uniform, fine, free-flowing powder, often de-agglomerated. | Can be dried to a low final moisture level, but without fine de-agglomeration. |
| Maintenance | More complex due to agitators and cyclones. | Generally lower maintenance due to a simpler mechanical design. |
| Key Advantage | Ideal for heat-sensitive, sticky, and lumpy materials requiring rapid drying. | Best for large-scale, continuous, and robust material processing. |
| Best Suited For | Pharmaceuticals, pigments, food additives, fine chemicals, and materials that degrade under prolonged heat. | Minerals, fertilizers, bulk chemicals, wood chips, and materials that are not easily degraded by heat. |