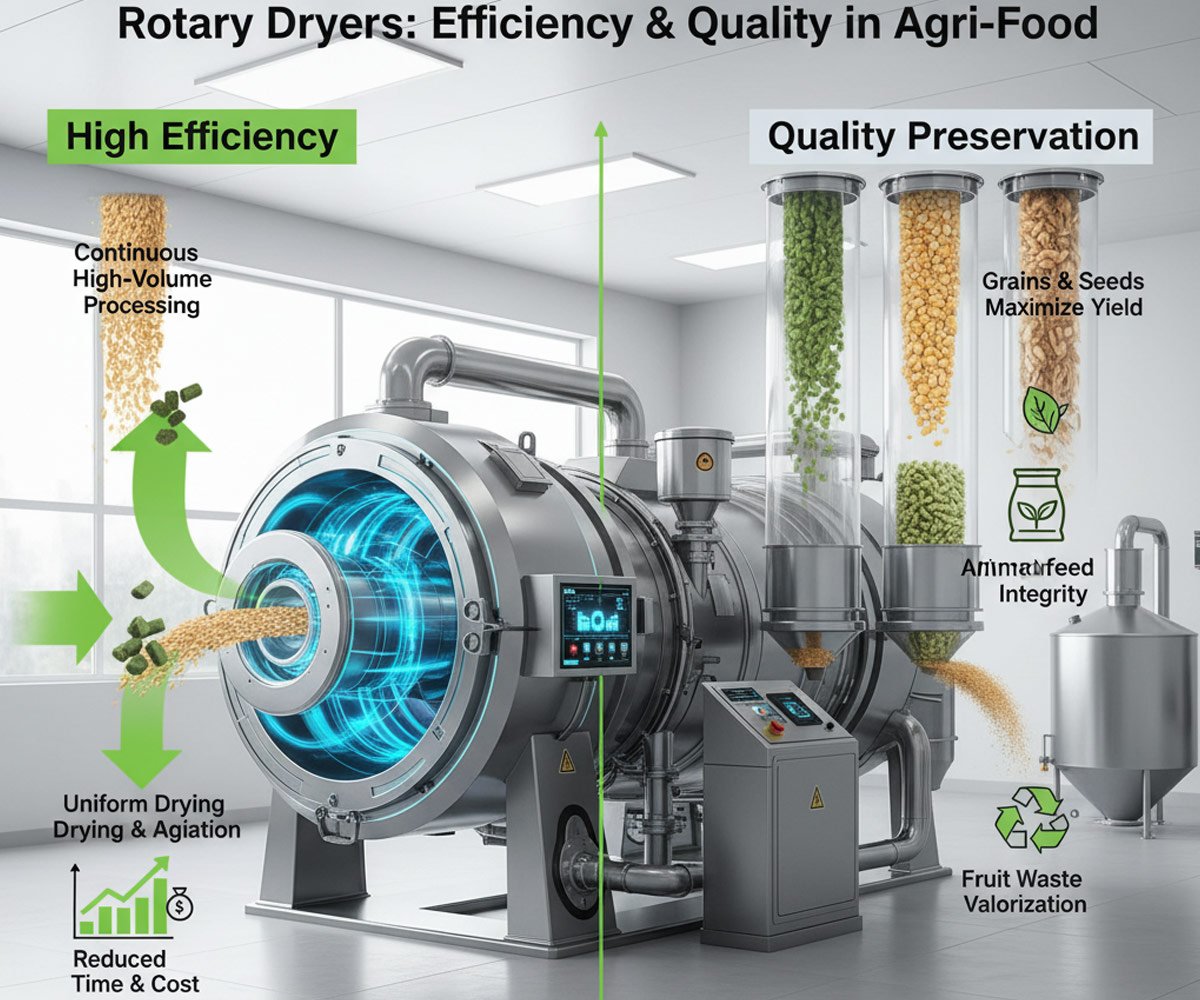
Rotary dryers are indispensable in the agriculture and food processing sectors, primarily because of their ability to handle enormous volumes of material continuously while providing uniform and controlled drying. This simultaneously improves efficiency, preserves product quality, and significantly minimizes post-harvest losses.
Efficiency Improvement Through Rotary Dryers
Rotary dryers are cylindrical, rotating drums with internal flights (lifters). As the drum rotates, the flights lift the material and cascade it through a stream of hot air, maximizing the surface area contact and ensuring highly efficient heat transfer.
- High Throughput & Continuous Operation: Rotary dryers are designed for continuous, large-scale production, making them ideal for handling the massive volumes of commodities produced during harvest seasons (e.g., grain) or daily production (e.g., animal feed). This continuous nature drastically improves plant efficiency compared to batch drying methods.
- Uniform Drying: The cascading action constantly tumbles and mixes the material. This physical agitation prevents hot spots and ensures every particle is exposed uniformly to the heated air, resulting in a consistent final moisture content across the entire batch. Uniform drying is a major factor in process efficiency.
- Flexibility with Feedstock: These dryers can efficiently handle materials with a wide range of moisture contents, particle sizes, and flow properties, from granules and powders to slurries and sticky fruit wastes.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: By quickly reducing the moisture content of the bulk material, the overall weight and volume of the product are lowered, leading to significant savings in storage and logistics.
Specific Applications and Quality Preservation
Rotary dryers play a vital role in preserving the quality of various agricultural and food products:9
| Application Sector | Materials Processed | Role in Efficiency and Quality Preservation |
| Grains and Seeds | Corn, Wheat, Soybean, Cereal Grains | Preservation: Rapidly reducing moisture content immediately after harvest prevents spoilage, mold growth, and insect infestation, which are major causes of post-harvest loss. Quality: Drying seeds uniformly preserves their viability and germination capacity. |
| Animal Feed | Distiller’s Dried Grains with Solubles (DDGS), Oilseeds, Citrus Pulp | Nutritional Integrity: Controlled drying temperatures (often using counter-current flow for heat-sensitive materials) are vital for preserving the nutritional value (vitamins, proteins) of feed ingredients. Shelf Life: Reducing moisture inhibits microbial growth, leading to a much longer shelf life for finished feed. |
| Fruit/Food Waste | Fruit Pomace (e.g., from apples, grapes, citrus), Brewer’s Spent Grain | Waste Valorization: Transforming high-moisture byproducts (which are costly to dispose of) into value-added materials, such as animal fodder or ingredients for pectin extraction. This closes the resource loop and significantly improves overall plant economics. |
| Fertilizers | Organic Manure, Compound Fertilizers (NPK, DAP) | Product Quality: Drying prevents the fertilizer granules from caking or clumping together, making them easier to store, transport, and spread evenly in the field, thus maintaining the effectiveness of the product. |
In summary, the robustness and high-capacity continuous operation of rotary dryers make them a foundational technology for achieving food security and economic viability in agriculture and food processing by effectively minimizing waste and maximizing product quality.
Would you like to know more about the different types of rotary dryers (direct vs. indirect) and which materials they are best suited for?