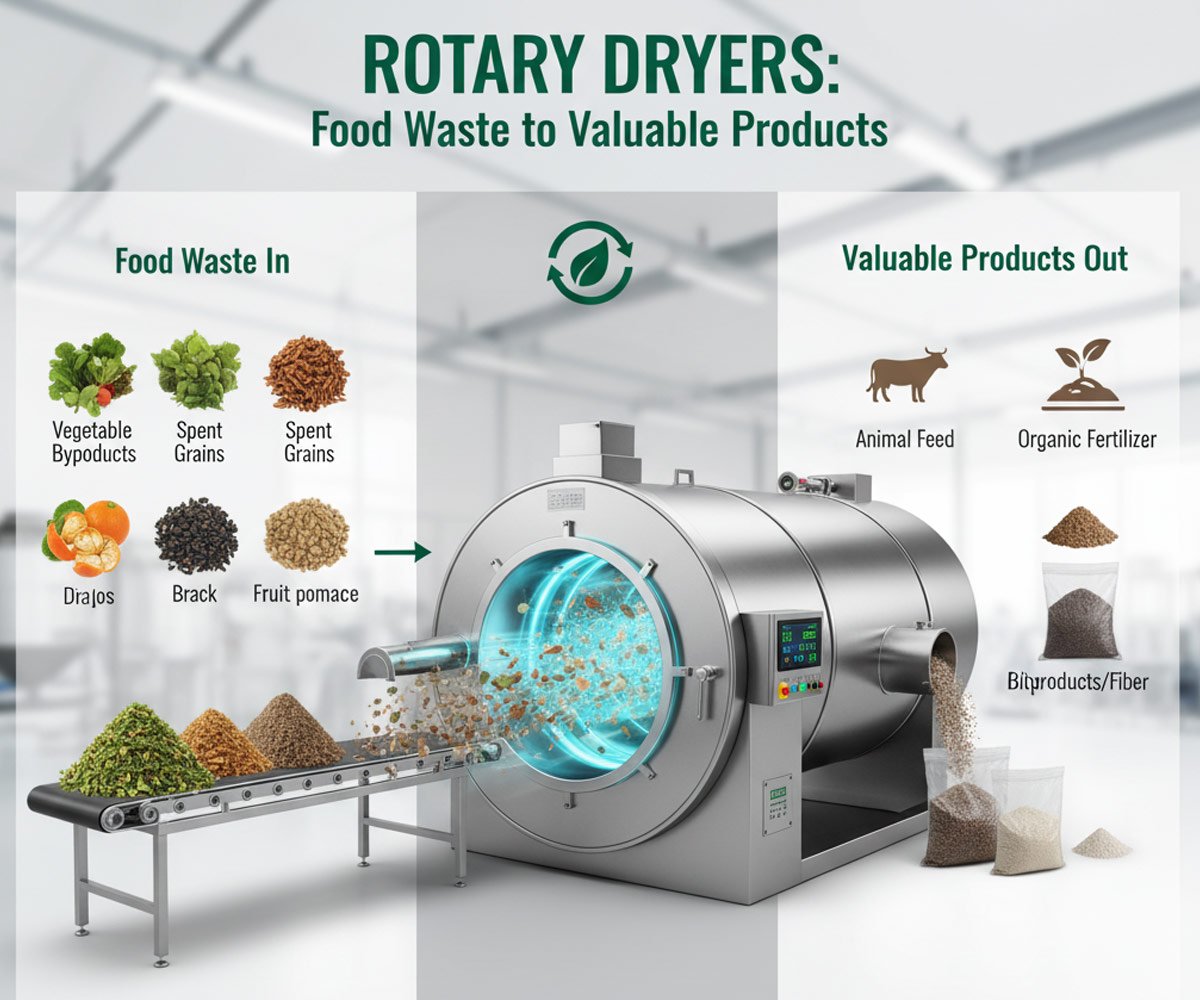
Food waste and byproducts from processing operations are often high in moisture, making them heavy, prone to spoilage, and costly to dispose of. Rotary dryers provide a robust, high-capacity method to reduce this moisture, transforming waste into stable, marketable products for various applications, thereby promoting sustainability and generating revenue.
1. Drying Vegetable Trimmings and Processing Residues
- Waste Source: Trimmings from vegetable processing (e.g., potato peels, carrot tops, outer leaves of cabbage), pulp from juicing operations, cannery waste.
- Challenge: High moisture content (often 70-90%), rapid spoilage, bulkiness.
- Rotary Dryer’s Role: The dryer efficiently removes moisture, converting the bulky, perishable waste into a concentrated, shelf-stable powder or granular product.
- Valuable Products:
- Animal Feed: Dried vegetable residues are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them excellent supplements for livestock feed.
- Compost Enhancers/Fertilizers: Dried and ground, they can be used as nutrient-rich organic soil amendments or as an ingredient in commercial fertilizers.
- Biogas Production (Pre-treatment): While not the final product, drying can sometimes be a pre-treatment step to optimize subsequent biogas digestion.
- Sustainability Benefit: Reduces landfill waste, creates a circular economy for nutrients, and lowers disposal costs for processors.
2. Drying Citrus Peel and Other Fruit Pomace
- Waste Source: Peels, seeds, and pulp leftover from fruit juice extraction (e.g., oranges, apples, grapes, tomatoes). This is a massive waste stream in the beverage industry.
- Challenge: High moisture, high acidity (citrus), stickiness (sugars), rapid fermentation.
- Rotary Dryer’s Role: Can handle the sticky nature of fruit pomace (often with the addition of recycle material) and effectively reduce moisture to create a stable product. Sometimes, a “flash dryer” (a type of pneumatic dryer) is combined with a rotary dryer for highly sticky materials.
- Valuable Products:
- Animal Feed (e.g., Citrus Pulp Pellets): Dried citrus pulp is a globally traded feed ingredient for cattle, valued for its energy and fiber content.
- Pectin and Fiber Extraction: Drying is a crucial step before extracting high-value compounds like pectin (a gelling agent) or dietary fiber from fruit residues.
- Biofuel (Pellets): Dried fruit pomace can be densified into pellets for use as biomass fuel.
- Sustainability Benefit: Transforms a high-volume, potentially polluting waste stream into a revenue-generating product, reducing environmental burden and contributing to animal nutrition.
3. Drying Brewer’s Spent Grain (BSG) and Distiller’s Grains
- Waste Source: Malted barley residue from breweries (BSG) and grain residues from distilleries (DDGS – Distiller’s Dried Grains with Solubles).
- Challenge: Very high moisture content (often 75-80% for BSG), perishable nature, bulky.
- Rotary Dryer’s Role: Efficiently dries these materials to create a stable, storable product. Often uses direct heating due to the robust nature of the material.
- Valuable Products:
- High-Protein Animal Feed: Both dried BSG and DDGS are excellent sources of protein and fiber for livestock (cattle, poultry, aquaculture), significantly reducing feed costs for farmers.
- Human Food Ingredients: Research is ongoing to use dried BSG as a fiber and protein-rich flour for baked goods.
- Sustainability Benefit: Converts a major byproduct of the brewing/distilling industry into a valuable feedstuff, contributing to a circular economy and reducing reliance on virgin feed sources.
By transforming these moist, perishable wastes into shelf-stable, value-added commodities, rotary dryers enable the food industry to enhance sustainability, reduce environmental footprint, and unlock new revenue streams.